
又到了1月份。新年伊始,寒风呼啸,呼吸道感染疾病频发。随着流感、新冠病毒、呼吸道合胞病毒(RSV)和胃肠道疾病诺如病毒这四种病毒在全美传播,你很难确定自己的病因到底是什么。再加上普通感冒,你会产生一系列类似的症状。
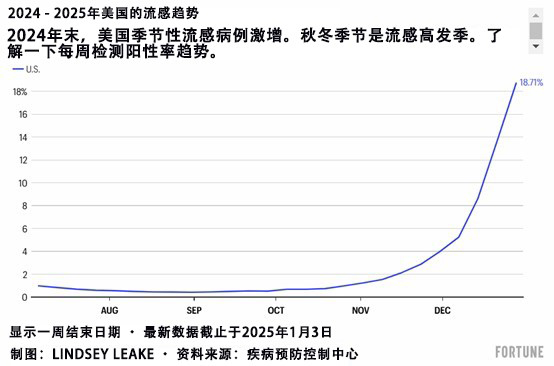
当前正是流感高发季。根据美国疾病预防控制中心(Centers for Disease Control and Prevention ,CDC)的数据,截至去年12月28日当周,全美流感检测阳性率达到了18.7%的季节性高点,而六周前这一数字仅为2.1%。此外,在该机构监测的所有10个地区的流感样疾病活动都有所上升。那么,如何确定自己得了流感呢?
与感染新冠一样,检测是确诊是否感染流感病毒的唯一方法。然而,疾控中心指出,医生可能仅根据患者的症状进行诊断。更准确的流感检测方法,如逆转录-聚合酶链式反应(RT-PCR)、病毒培养和荧光免疫检测等,需要医疗保健人员在患者喉咙深处或鼻腔内部进行拭子采样,然后将拭子送到专业实验室。
而流感快速诊断检测(RIDT)和快速分子检测虽然准确度较差,但更容易操作。在许多药店、大卖场和在线零售商处都能买到RIDT检测产品。如果你无法自行检测,急诊中心、医疗检测机构和其他诊所都可以为你进行检测,在10到20分钟内就能得到结果,具体时间取决于检测类型。
一些非处方检测产品和实验室检测可以在一个样本中区分出新冠病毒、甲型流感病毒、乙型流感病毒和/或呼吸道合胞病毒。虽然同时患流感和其他呼吸道疾病的可能性是存在的,但疾控中心表示尚不清楚这种情况的普遍性。
流感有哪些症状?
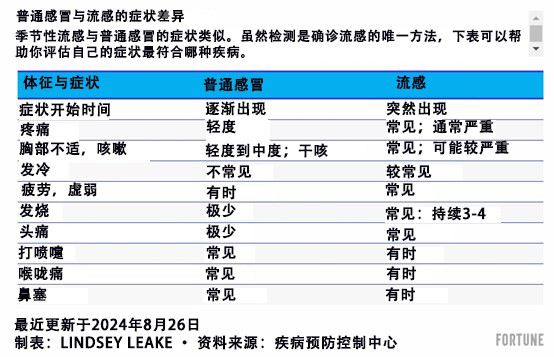
知道自己是否患有某种呼吸道疾病不仅有助于公共卫生官员追踪疾病传播情况,还能帮助医疗保健人员为你确定最佳治疗方案。疾控中心指出,如果你有以下症状,你可能需要考虑进行流感检测:
• 咳嗽
• 疲劳
• 发烧或感觉发烧/发冷(并非所有人都会发烧)
• 头痛
• 肌肉痛或身体疼痛
• 流鼻涕或鼻塞
• 喉咙痛
• 呕吐和腹泻(儿童更常见症状)
哪些流感症状需要紧急就医?
大多数人感染流感后仅有上述轻微症状,并且无需使用抗病毒处方药即可自行康复。然而,对老年人、幼儿以及哮喘、肥胖症和心脏病等病症的患者来说,流感仍然可能引发重症甚至致命。
洛杉矶西达赛奈医疗中心(Cedars-Sinai Medical Center)的医院流行病学副医疗主任迈克尔·本-阿德雷特博士此前对《财富》杂志表示:“美国每年有成千上万的患者因流感住院和死亡,特别是老年人或其他疾病的患者。对这些人和其他所有人来说,最好接种流感疫苗。”
如果你或你照顾的人出现以下任何流感并发症的迹象,疾控中心建议紧急就医:
• 成年人
o 呼吸困难或气短
o 发烧或咳嗽好转后复发或恶化
o 无尿
o 持续头晕、意识不清、无法唤醒
o 胸腹部持续疼痛或压迫感
o 惊厥
o 严重肌肉疼痛
o 严重虚弱或不稳
o 慢性病恶化
• 儿童
o 12周以下儿童发烧
o 嘴唇或脸色发青
o 胸痛
o 脱水(8小时无尿、口干、哭泣时无泪)
o 呼吸急促或呼吸困难
o 高烧超过104华氏度,且退烧药无效
o 发烧或咳嗽好转后复发或恶化
o 清醒时反应迟钝或没有正常互动
o 每次呼吸时肋骨内陷
o 惊厥
o 严重肌肉疼痛(孩子拒绝走路)
o 慢性病恶化
1月份接种流感疫苗是否为时已晚?
美国国家传染病基金会(National Foundation for Infectious Diseases)的医疗主任罗伯特·霍普金斯博士表示,简单来说,一点都不晚。
霍普金斯在12月份对《财富》杂志表示:“根本不晚。当未来面临风险时,任何时候接种疫苗都是有益的。我当然希望人们能更早接种疫苗,但我不会为了追求完美而忽视任何时候接种疫苗的好处。”
尽管2024至2025年的季节性流感疫苗不能预防H5N1禽流感,但疾控中心表示,接种疫苗的人越多,当前的禽流感爆发成为大流行的可能性就越低。这是因为两种类型的流感可能交换遗传物质,形成一种新的流感病毒,并在人类中传播。
然而,今年流感季的疫苗接种覆盖率一直不足。截至去年12月28日当周,只有不到一半的成年人(42.7%)接种了年度流感疫苗,儿童的比例也相差无几(41.9%)。(财富中文网)
译者:刘进龙
审校:汪皓
又到了1月份。新年伊始,寒风呼啸,呼吸道感染疾病频发。随着流感、新冠病毒、呼吸道合胞病毒(RSV)和胃肠道疾病诺如病毒这四种病毒在全美传播,你很难确定自己的病因到底是什么。再加上普通感冒,你会产生一系列类似的症状。
当前正是流感高发季。根据美国疾病预防控制中心(Centers for Disease Control and Prevention ,CDC)的数据,截至去年12月28日当周,全美流感检测阳性率达到了18.7%的季节性高点,而六周前这一数字仅为2.1%。此外,在该机构监测的所有10个地区的流感样疾病活动都有所上升。那么,如何确定自己得了流感呢?
与感染新冠一样,检测是确诊是否感染流感病毒的唯一方法。然而,疾控中心指出,医生可能仅根据患者的症状进行诊断。更准确的流感检测方法,如逆转录-聚合酶链式反应(RT-PCR)、病毒培养和荧光免疫检测等,需要医疗保健人员在患者喉咙深处或鼻腔内部进行拭子采样,然后将拭子送到专业实验室。
而流感快速诊断检测(RIDT)和快速分子检测虽然准确度较差,但更容易操作。在许多药店、大卖场和在线零售商处都能买到RIDT检测产品。如果你无法自行检测,急诊中心、医疗检测机构和其他诊所都可以为你进行检测,在10到20分钟内就能得到结果,具体时间取决于检测类型。
一些非处方检测产品和实验室检测可以在一个样本中区分出新冠病毒、甲型流感病毒、乙型流感病毒和/或呼吸道合胞病毒。虽然同时患流感和其他呼吸道疾病的可能性是存在的,但疾控中心表示尚不清楚这种情况的普遍性。
流感有哪些症状?
知道自己是否患有某种呼吸道疾病不仅有助于公共卫生官员追踪疾病传播情况,还能帮助医疗保健人员为你确定最佳治疗方案。疾控中心指出,如果你有以下症状,你可能需要考虑进行流感检测:
• 咳嗽
• 疲劳
• 发烧或感觉发烧/发冷(并非所有人都会发烧)
• 头痛
• 肌肉痛或身体疼痛
• 流鼻涕或鼻塞
• 喉咙痛
• 呕吐和腹泻(儿童更常见症状)
哪些流感症状需要紧急就医?
大多数人感染流感后仅有上述轻微症状,并且无需使用抗病毒处方药即可自行康复。然而,对老年人、幼儿以及哮喘、肥胖症和心脏病等病症的患者来说,流感仍然可能引发重症甚至致命。
洛杉矶西达赛奈医疗中心(Cedars-Sinai Medical Center)的医院流行病学副医疗主任迈克尔·本-阿德雷特博士此前对《财富》杂志表示:“美国每年有成千上万的患者因流感住院和死亡,特别是老年人或其他疾病的患者。对这些人和其他所有人来说,最好接种流感疫苗。”
如果你或你照顾的人出现以下任何流感并发症的迹象,疾控中心建议紧急就医:
• 成年人
o 呼吸困难或气短
o 发烧或咳嗽好转后复发或恶化
o 无尿
o 持续头晕、意识不清、无法唤醒
o 胸腹部持续疼痛或压迫感
o 惊厥
o 严重肌肉疼痛
o 严重虚弱或不稳
o 慢性病恶化
• 儿童
o 12周以下儿童发烧
o 嘴唇或脸色发青
o 胸痛
o 脱水(8小时无尿、口干、哭泣时无泪)
o 呼吸急促或呼吸困难
o 高烧超过104华氏度,且退烧药无效
o 发烧或咳嗽好转后复发或恶化
o 清醒时反应迟钝或没有正常互动
o 每次呼吸时肋骨内陷
o 惊厥
o 严重肌肉疼痛(孩子拒绝走路)
o 慢性病恶化
1月份接种流感疫苗是否为时已晚?
美国国家传染病基金会(National Foundation for Infectious Diseases)的医疗主任罗伯特·霍普金斯博士表示,简单来说,一点都不晚。
霍普金斯在12月份对《财富》杂志表示:“根本不晚。当未来面临风险时,任何时候接种疫苗都是有益的。我当然希望人们能更早接种疫苗,但我不会为了追求完美而忽视任何时候接种疫苗的好处。”
尽管2024至2025年的季节性流感疫苗不能预防H5N1禽流感,但疾控中心表示,接种疫苗的人越多,当前的禽流感爆发成为大流行的可能性就越低。这是因为两种类型的流感可能交换遗传物质,形成一种新的流感病毒,并在人类中传播。
然而,今年流感季的疫苗接种覆盖率一直不足。截至去年12月28日当周,只有不到一半的成年人(42.7%)接种了年度流感疫苗,儿童的比例也相差无几(41.9%)。(财富中文网)
译者:刘进龙
审校:汪皓
Ah, January. The season of new beginnings, icy winds, and respiratory infections. With a “quad-demic” of diseases circulating the country—flu, COVID, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and norovirus, a gastrointestinal illness—it can be difficult to be sure which is making you sick. Throw in the common cold, and you’ve got a symphony of similar symptoms.
The flu is having a moment. Nationwide test positivity was at a season-high 18.7% the week ended Dec. 28, compared to 2.1% six weeks earlier, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). What’s more, influenza-like illness activity was elevated in all 10 regions the agency surveils. So how can you be sure you have the flu?
As with COVID, testing is the only way to confirm the presence of the influenza virus in your body. However, the CDC notes that your doctor may diagnose you based on your symptoms alone. The more accurate flu tests—reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), viral culture, and immunofluorescence assays—require a health care provider to swipe the back of your throat or the inside of your nose, then send the swab to a specialized lab.
While less accurate, rapid influenza diagnostic tests (RIDTs) and rapid molecular assays are more accessible. You can purchase an RIDT over the counter at a number of pharmacies, big-box stores, and online retailers. If you’re unable to complete such testing on your own, urgent care centers, medical testing facilities, and other clinics can do it for you and provide results within 10 to 20 minutes, depending on the type of test.
Some over-the-counter and laboratory tests can differentiate between COVID, influenza A, influenza B, and/or RSV in a single sample. It’s also possible to have flu and another respiratory illness at the same time, though the CDC says it’s unclear how common this is.
What are the symptoms of the flu?
Knowing which respiratory illness you do or don’t have not only assists public health officials in tracking disease spread, but also helps your health care provider determine the best course of treatment for you. You might consider flu testing if you have the following symptoms, as noted by the CDC:
• Cough
• Fatigue
• Fever or feeling feverish/chills (not everyone will have a fever)
• Headaches
• Muscle or body aches
• Runny or stuffy nose
• Sore throat
• Vomiting and diarrhea (more common in children)
Which flu symptoms require emergency care?
Most people who catch the flu have only the above mild symptoms and recover on their own without the use of antiviral prescription medication. Still, flu can be serious and even deadly for older adults, young children, and people with certain conditions including asthma, obesity, and heart disease.
“Every year in this country we have thousands and thousands of patients who are hospitalized and die with influenza, and they are particularly older people or people with medical illness,” Dr. Michael Ben-Aderet, associate medical director of hospital epidemiology at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles, previously told Fortune. “It is beneficial to those people and everyone else that we get the flu vaccine.”
If you or a person in your care shows any of the following signs of flu complications, the CDC recommends seeking emergency medical care:
• Adults
o Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath
o Fever or cough that improves but then returns or worsens
o Not urinating
o Persistent dizziness, confusion, inability to arouse
o Persistent pain or pressure in the chest or abdomen
o Seizures
o Severe muscle pain
o Severe weakness or unsteadiness
o Worsening of chronic medical conditions
• Children
o Any fever in children younger than 12 weeks
o Bluish lips or face
o Chest pain
o Dehydration (no urine for 8 hours, dry mouth, no tears when crying)
o Fast breathing or trouble breathing
o Fever above 104 degrees that’s not controlled by fever-reducing medicine
o Fever or cough that improves but then returns or worsens
o Not alert or interacting when awake
o Ribs pulling in with each breath
o Seizures
o Severe muscle pain (child refuses to walk)
o Worsening of chronic medical conditions
Is January too late to get the flu shot?
In a word, no, says Dr. Robert Hopkins Jr., medical director of the National Foundation for Infectious Diseases.
“It’s not too late,” Hopkins told Fortune in December. “It is not a bad time when we’ve got risk in front of us. And I would certainly prefer that people were vaccinated earlier, but I’m not going to make perfection the enemy of the good.”
And while the 2024–25 seasonal flu vaccine doesn’t protect against H5N1 bird flu, the more people who get the vaccine, the lower the chances of the current bird flu outbreak becoming a pandemic, the CDC says. That’s because it’s possible for the two flu types to exchange genetic material, forming a new flu virus that could spread among humans.
Yet vaccination coverage this season has been lacking. Less than half of adults (42.7%) had gotten their annual flu shot as of the week ended Dec. 28, as had about the same proportion of children (41.9%).






